The Role of the Right Ventricle in Heart Failure
This article looks at the role of the right ventricle in heart failure, exploring a 1943 study that concluded its weakness was less important, and how this was later disproven.

NEJM
The New England Journal of Medicine (https://t.co/YGfDrRsIhE) is the world’s leading medical journal and website.
-
A 1943 study concluded that “weakness of the right side of the heart…seems less important” in the dynamics of #HeartFailure. A similar conclusion was drawn from the success of the Fontan procedure in patients with congenital heart disease. 1/13
— NEJM (@NEJM) March 24, 2023 -
It was later shown that healthy patients who have undergone the Fontan procedure have a 40% decrease in exercise capacity, a finding that speaks to the relevance of the right ventricle even in healthy persons. 2/13
— NEJM (@NEJM) March 24, 2023 -
We also now know that the right ventricle plays a critical pathophysiological and prognostic role in numerous conditions, including left heart failure, pulmonary arterial hypertension, and even #SARSCov2. 3/13
— NEJM (@NEJM) March 24, 2023 -
The main determinants of right ventricular function, like those of left ventricular function, are preload, afterload, contractility, and lusitropy. 4/13
— NEJM (@NEJM) March 24, 2023 -
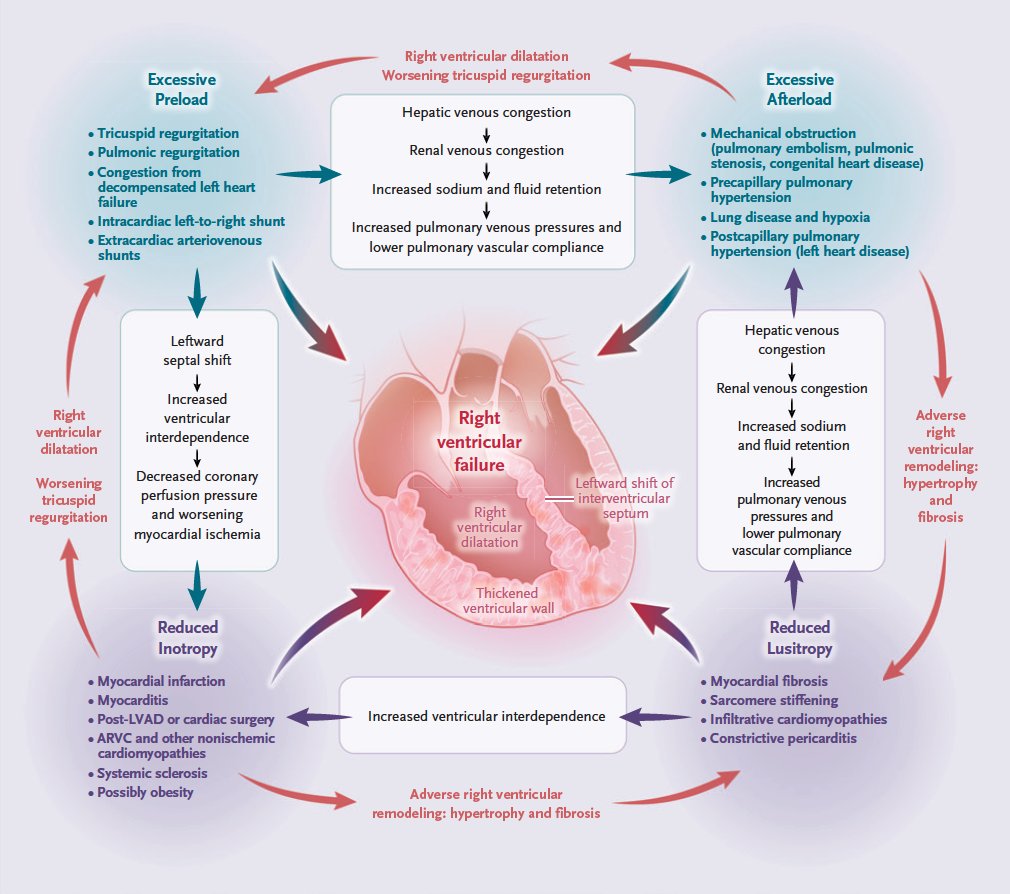
The pathophysiological mechanisms of right ventricular failure can be conceptualized as acute or chronic abnormalities of right ventricular load or myocardial function, though in clinical states of right ventricular failure, these mechanisms frequently coexist. 5/13 pic.twitter.com/1iVTE6VSZZ
— NEJM (@NEJM) March 24, 2023 -
Pathophysiological processes that initiate or promote right ventricular failure include myocyte hypertrophy, fibrosis, ischemia, neurohormonal activation, inflammation, and shifts in metabolic substrates. 6/13 pic.twitter.com/1LS2MLHFql
— NEJM (@NEJM) March 24, 2023 -
Most data on molecular mechanisms of right ventricular failure are derived from animal models or clinical studies of pulmonary arterial hypertension. The degree to which these findings apply to other causes of right ventricular failure is unknown. 7/13
— NEJM (@NEJM) March 24, 2023 -
The reference standard for assessing right ventricular contractility and function relies on pressure–volume relationships and the creation of pressure–volume loops with the use of conductance catheters in the catheterization laboratory. 8/13
— NEJM (@NEJM) March 24, 2023 -
The pressure–volume loop represents a single cardiac cycle, with the width of the loop representing stroke volume. 9/13 pic.twitter.com/29qBGp6qEO
— NEJM (@NEJM) March 24, 2023 -
Patients with suspected right ventricular dysfunction should undergo transthoracic echocardiography, which can provide a rapid assessment of right ventricular size and function and an estimate of pulmonary-artery systolic pressure (PASP) in most patients. 10/13
— NEJM (@NEJM) March 24, 2023 -
Several quantitative measures of right ventricular function are easy to obtain, are reproducible, and have prognostic value, including the tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion (TAPSE). 11/13
— NEJM (@NEJM) March 24, 2023 -
In addition, echocardiography can be used to calculate the TAPSE:PASP ratio, which has been shown to be at least moderately correlated with the reference standard of right ventricular–pulmonary arterial coupling. 12/13 pic.twitter.com/avAtS84Nr2
— NEJM (@NEJM) March 24, 2023 -
Read the full Review Article “Right Ventricular Failure” by Brian A. Houston, M.D., Evan L. Brittain, M.D., and Ryan J. Tedford, M.D.: https://t.co/49H4frwEQI 13/13#Cardiology
— NEJM (@NEJM) March 24, 2023
