Exploring the Molecular Pathogenesis of Neurodegenerative Diseases
Neurodegenerative diseases are commonly adult-onset conditions characterized by degeneration of specific neuronal populations. Aberrant messenger RNA (mRNA) translation is implicated in a range of neurodegenerative diseases, including Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease and others. This article explores the molecular pathogenesis of these diseases and the lack of effective treatments.

NEJM
The New England Journal of Medicine (https://t.co/YGfDrRsIhE) is the world’s leading medical journal and website.
-
Neurodegenerative diseases are commonly adult-onset conditions characterized by degeneration of specific neuronal populations. Familial forms are caused by mutations in single genes, but most patients have a sporadic form that lacks a clear correlative mutation. 1/10
— NEJM (@NEJM) March 20, 2023 -
Many of these diseases are characterized by abnormal protein aggregates with a unique molecular composition for each disease. The molecular pathogenesis of these diseases remains largely enigmatic. Consequently, effective disease-modifying treatments are generally lacking. 2/10
— NEJM (@NEJM) March 20, 2023 -
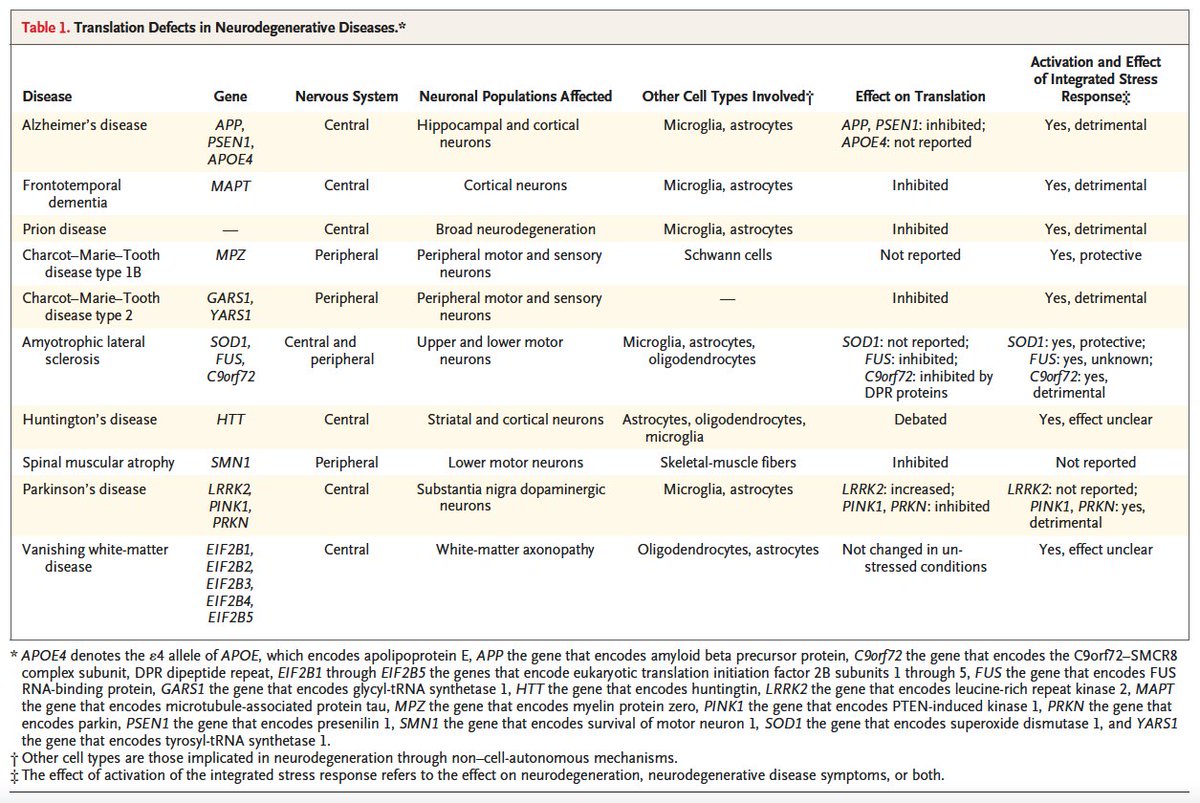
Aberrant messenger RNA (mRNA) translation is implicated in a range of neurodegenerative diseases, including Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease and others. 3/10 pic.twitter.com/hTwcCUpoDD
— NEJM (@NEJM) March 20, 2023 -
The integrated stress response is a signaling pathway that allows cells to cope with cellular stress by altering gene expression. Many different stressors may activate this response. 4/10
— NEJM (@NEJM) March 20, 2023 -
A hallmark of the integrated stress response is phosphorylation of the α subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 (eIF2), mediated by one of four eIF2α kinases that act as sensors of distinct forms of cellular stress. 5/10 pic.twitter.com/AT3PgeCufB
— NEJM (@NEJM) March 20, 2023 -
The ternary complex of eIF2 (consisting of α, β, and γ subunits) with guanosine triphosphate (GTP) and the initiator transfer RNA (tRNAi Met) binds to the 40S ribosomal subunit on the mRNA to facilitate interaction with the AUG initiation codon. 6/10
— NEJM (@NEJM) March 20, 2023 -
On AUG recognition, GTP is hydrolyzed to guanosine diphosphate (GDP). The guanine nucleotide exchange factor eIF2B catalyzes the nucleotide exchange of eIF2-GDP into eIF2-GTP, which is rate limiting for ternary complex formation and function. 7/10
— NEJM (@NEJM) March 20, 2023 -
A decameric (10-component) complex, eIF2B is composed of two heteropentamers consisting of α, β, γ, δ, and ε subunits, of which the ε subunit harbors the catalytic guanine nucleotide exchange activity. 8/10
— NEJM (@NEJM) March 20, 2023 -
Whereas nonphosphorylated eIF2 is a substrate for eIF2B, phosphorylation of eIF2α converts eIF2 from an activator into an inhibitor of eIF2B. Thus, eIF2α phosphorylation causes inhibition of global mRNA translation by reducing the amount of the ternary complex. 9/10 pic.twitter.com/gbC7OUJmGm
— NEJM (@NEJM) March 20, 2023 -
To learn more, read “Messenger RNA Translation Defects in Neurodegenerative Diseases” by Erik Storkebaum, Ph.D., Kobi Rosenblum, Ph.D., and Nahum Sonenberg, Ph.D.: https://t.co/UFDMnASUhw 10/10
— NEJM (@NEJM) March 20, 2023
