Estimating Fitness Effects of SARS-CoV-2 Mutations
This blog discusses SARS-CoV-2 trackers and their speculation on ORF9b mutations in recent variants. It also provides an update on previously described work estimating fitness effects of amino-acid mutations to all SARS-CoV-2 proteins.

Bloom Lab
Lab studying molecular evolution of proteins and viruses. Affiliated with @fredhutch @HHMINEWS @uwgenome. @jbloom_lab@mstdn.science
-
Minor update to our previously described work estimating fitness effects of amino-acid mutations to all SARS-CoV-2 proteins (https://t.co/70y9VXAoES):
— Bloom Lab (@jbloom_lab) March 16, 2023
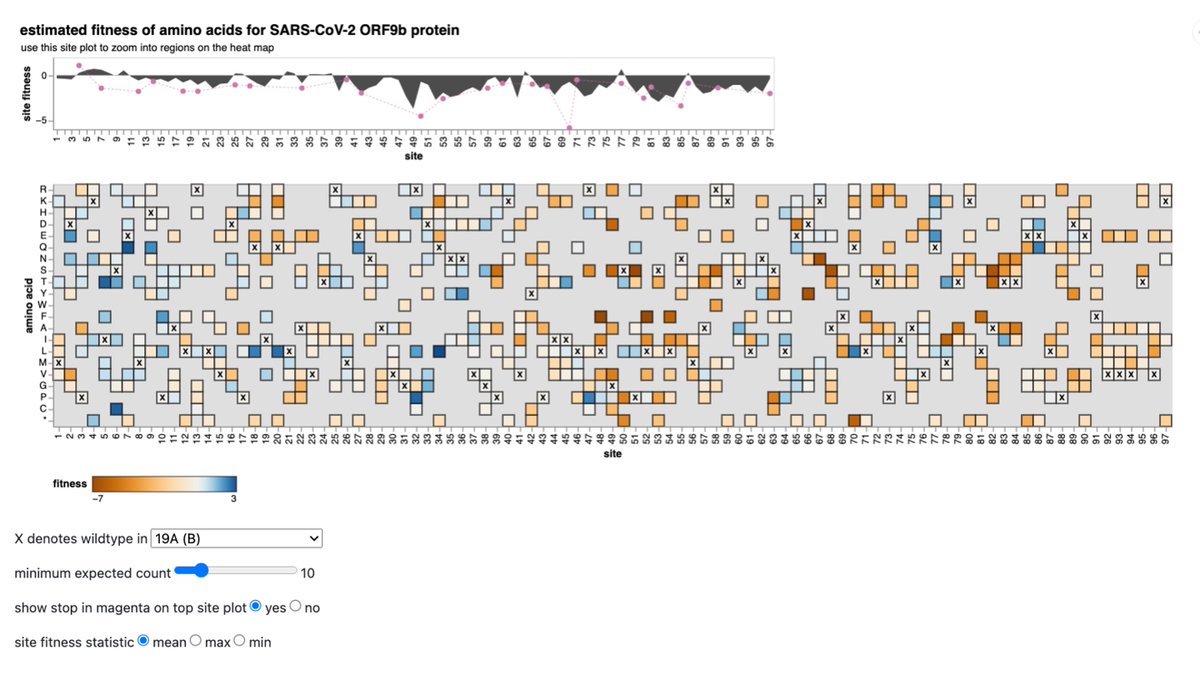
We have added estimates for the ORF9b accessory protein, which is encoded in overlapping reading frame in N gene. -
SARS-CoV-2 trackers (eg, @SolidEvidence @siamosolocani @dfocosi) speculate ORF9b mutations maybe relevant in recent variants (https://t.co/5CdOyPv54i & https://t.co/sZPR4h9nRI)
— Bloom Lab (@jbloom_lab) March 16, 2023
I'm not sufficiently informed on ORF9b to offer opinion on whether they are correct. -
However, w help from @alchemytoday (https://t.co/CzmLeiWs33) I added estimates of fitness effects of ORF9b mutations based on their counts in natural SARS-CoV-2 sequences.
— Bloom Lab (@jbloom_lab) March 16, 2023
These estimates can be explored interactively at https://t.co/Zod11UMNqQ pic.twitter.com/dS55nDfDZ2 -
Caveat is that interpretation of the estimates above of effects of mutations to ORF9b is confounded with selection on alternate codon frames encoding N amino acids, since we know that N is an essential protein that is under strong constraint.
— Bloom Lab (@jbloom_lab) March 16, 2023 -
Remembering that caveat, we can see overall ORF9b is under relatively weak selection, similar to most other viral accessory proteins.
— Bloom Lab (@jbloom_lab) March 16, 2023
(Below and interactive version at https://t.co/HfTvd1jn3R) pic.twitter.com/f4uSaxAn2v -
I previously noted how accessory gene under strongest selection against premature stop codons is ORF3 (see plot in prior Tweet).
— Bloom Lab (@jbloom_lab) March 16, 2023
This corresponds w experiments showing measurable attenuation in lab for knocking out only ORF3 & not other accessory genes: https://t.co/DDa6Bndwd2 -
The plot two Tweets prior suggests ORF9b is under only weak purifying selection against premature truncation.
— Bloom Lab (@jbloom_lab) March 16, 2023
This makes ORF9b similar to all the non-ORF3a accessory proteins that were experimentally measured to not have strong effects on viral growth in lab. -
But natural selection is much more sensitive than any lab experiment, and most ORF9b premature stops do have a measurably negative effect on viral fitness in humans (although confounded with N selection).
— Bloom Lab (@jbloom_lab) March 16, 2023
So it's possible ORF9b mutations could play some role in variant fitness.
