CLEAR Outcomes Trial: Evaluating Bempedoic Acid in Cardiovascular Disease
In the NEJM, Nissen et al. report the results of the CLEAR Outcomes trial, which tested the effect of bempedoic acid in patients with or at increased risk for cardiovascular disease. Statins are typically used as first-line agents to prevent cardiovascular events in these patients, but the trial found that bempedoic acid could reduce LDL cholesterol levels.

NEJM
The New England Journal of Medicine (https://t.co/YGfDrRsIhE) is the world’s leading medical journal and website.
-
In NEJM, Nissen et al. report the results of the CLEAR Outcomes trial, which tested the effect of bempedoic acid in patients with or at increased risk for #CardiovascularDisease. Full trial results: https://t.co/2GIT1lJ5rJ
— NEJM (@NEJM) April 14, 2023
Read the editorial: https://t.co/Ck0XN4WYey 1/13 -
Patients who were unable or unwilling to take high-intensity statins because of unacceptable adverse effects were the target trial population; statins are typically used as first-line agents to prevent cardiovascular events in patients at high cardiovascular risk. 2/13
— NEJM (@NEJM) April 14, 2023 -
Nissen et al. found that the percent reduction in the LDL cholesterol level was 21 percentage points greater with bempedoic acid than with placebo. 3/13
— NEJM (@NEJM) April 14, 2023 -
This reduction in cholesterol level corresponded to a 13% lower risk of major adverse cardiovascular events, defined as a four-component composite of death from cardiovascular causes, nonfatal myocardial infarction, nonfatal stroke, or coronary revascularization. 4/13
— NEJM (@NEJM) April 14, 2023 -
These results are discussed in an accompanying editorial and are welcome news for a patient population in which it is otherwise challenging to achieve meaningful reductions in cholesterol levels & the risk of cardiovascular events. Read the editorial: https://t.co/5x9OEvNR9m 5/13
— NEJM (@NEJM) April 14, 2023 -
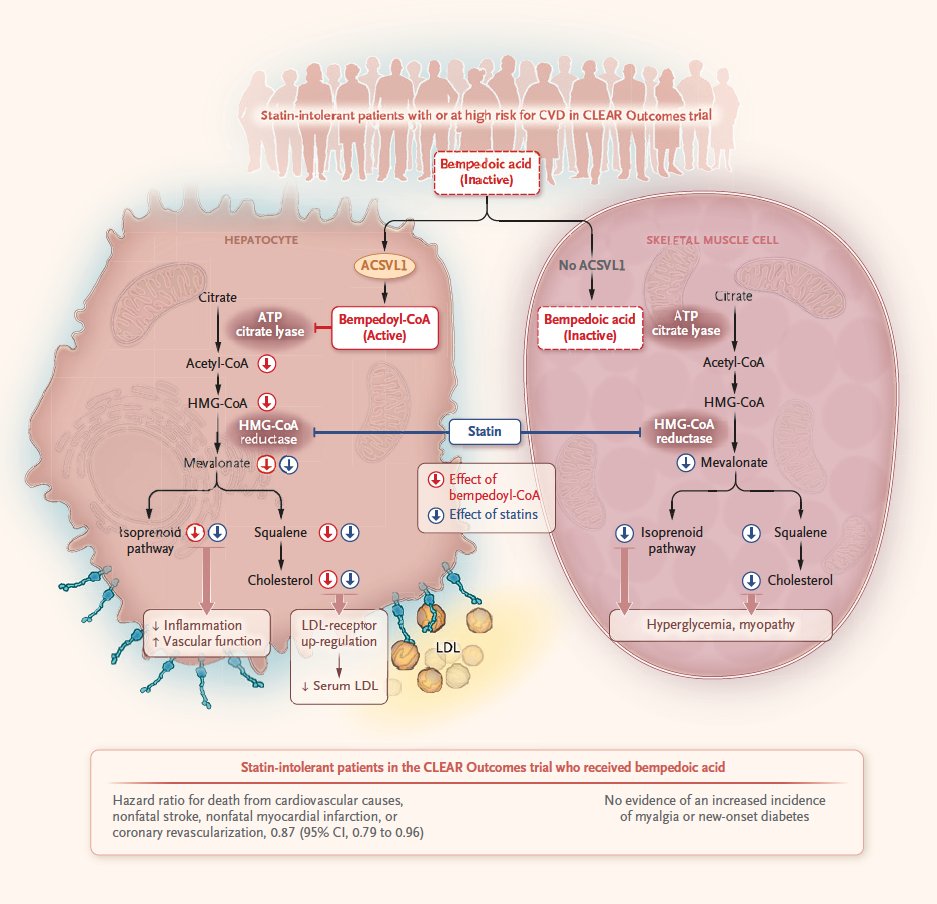
Statins derive their name from lovastatin, the first commercially available inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl–coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase, the rate-limiting enzyme of the mevalonate pathway that is responsible for cholesterol and isoprenoid synthesis. 6/13 pic.twitter.com/Lzens0xUsL
— NEJM (@NEJM) April 14, 2023 -
The inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase has implications beyond cholesterol synthesis. 7/13
— NEJM (@NEJM) April 14, 2023 -
This enzyme is also required for the isoprenoid pathway, which is needed for the synthesis of ubiquinol, and post-translational protein prenylation, which is essential for the cell-membrane attachment and function of many signaling proteins. 8/13 pic.twitter.com/dXcTyRltDW
— NEJM (@NEJM) April 14, 2023 -
On balance, statins have a very favorable therapeutic window, with the benefits far outweighing the risks. However, the ultimate benefit of statins can be limited by discontinuation of therapy because of unacceptable adverse effects. 9/13
— NEJM (@NEJM) April 14, 2023 -
Bempedoic acid is a prodrug: it requires conversion by the very-long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase 1 (ASCVL1) into a CoA-thioester that is the active metabolite. 10/13 pic.twitter.com/qkSvMs2ise
— NEJM (@NEJM) April 14, 2023 -
The CoA-thioester inhibits adenosine triphosphate citrate lyase that is in the cholesterol biosynthetic pathway upstream of HMG-CoA reductase. 11/13
— NEJM (@NEJM) April 14, 2023 -
Thus, through a mechanism distinct from that of statins, bempedoic acid inhibits the mevalonate pathway and produces a depletion of cellular cholesterol and subsequent up-regulation of hepatic LDL receptors to lower circulating LDL cholesterol levels. 12/13
— NEJM (@NEJM) April 14, 2023 -
Read “Bempedoic Acid and the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease” by John F. Keaney, Jr., M.D.: https://t.co/Ck0XN4WYey 13/13
— NEJM (@NEJM) April 14, 2023
